I did a home sleep test recently and this was the report. I thought I have sleep apnoea as my wife said thre are times when I sound like I am choking during sleep. AHI was normal but there were ...
The symptoms you are describing, such as a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen during urination, frequent urges to urinate, and difficulty passing urine, could be indicative of several potential conditions. Here are some possibilities: Potential Causes 1. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI): - UTIsRead more
The symptoms you are describing, such as a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen during urination, frequent urges to urinate, and difficulty passing urine, could be indicative of several potential conditions. Here are some possibilities:
Potential Causes
1. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI):
– UTIs can cause a frequent urge to urinate, discomfort, and a sensation of incomplete bladder emptying.
– Symptoms may include burning during urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and sometimes fever.
2. Bladder Spasms or Overactive Bladder:
– Characterized by sudden, involuntary contractions of the bladder muscle, leading to frequent urination and urgency.
3. Urinary Retention:
– This condition involves difficulty emptying the bladder completely. It can be acute or chronic and may be caused by blockages, nerve problems, or muscle dysfunction.
4. Prostatic Issues (in males):
– Conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) can lead to urinary retention and frequent urination.
5. Bladder Stones or Tumors:
– These can obstruct urine flow and cause similar symptoms.
Recommended Actions
1. Consult a Healthcare Professional:
– It’s important to see a doctor for a proper evaluation. They may perform a physical examination and recommend tests such as a urinalysis, ultrasound, or urodynamic studies to determine the underlying cause.
2. Medications:
– Antibiotics: If a UTI is diagnosed, antibiotics will be prescribed.
– Anticholinergics or Beta-3 Agonists: These medications can help manage symptoms of overactive bladder.
– Alpha-blockers: For males with prostatic issues, these can help relax the muscles of the prostate and bladder neck.
3. Precautions and Lifestyle Modifications:
– Hydration: Drink adequate water but avoid excessive fluid intake, especially before bedtime.
– Dietary Adjustments: Avoid bladder irritants such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods.
– Bladder Training: Practice scheduled urination to improve bladder control.
– Pelvic Floor Exercises: Strengthening pelvic muscles can help manage symptoms.
When to Seek Immediate Help
– If you experience severe pain, complete inability to urinate, or signs of a severe infection (e.g., high fever, chills), seek medical attention promptly.
Follow-Up
– Adhere to follow-up appointments to monitor your condition and adjust treatment as necessary. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting or changing any medication regimen.
Remember, while these suggestions can guide you, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice tailored to your specific situation.
See less
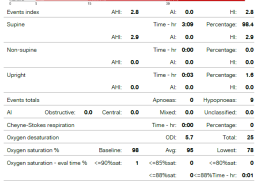
Based on your description, your home sleep test raises some potential concerns, despite a normal Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI). Here are some considerations and insights tailored to your situation: 1. Oxygen Desaturation Concerns: An oxygen saturation level dropping to 78% is significant. Normally, oxyRead more
Based on your description, your home sleep test raises some potential concerns, despite a normal Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI). Here are some considerations and insights tailored to your situation:
1. Oxygen Desaturation Concerns: An oxygen saturation level dropping to 78% is significant. Normally, oxygen saturation during sleep should remain above 90%. A desaturation to 78% can suggest episodes of hypoxemia. This finding warrants further investigation, as recurrent or severe hypoxemia can have adverse effects, including those on cardiovascular and neurocognitive health.
2. Hypopnea Episodes: The presence of hypopneas, even with a normal AHI, is noteworthy. It’s important to consider which criteria were used to define hypopneas, as some definitions emphasize oxygen desaturation while others focus on EEG arousals. Both can contribute to reduced sleep quality and daytime symptoms like fatigue and sleepiness.
3. Limitations of Home Sleep Tests: While home sleep tests can be convenient, they often have limitations in detecting certain types of sleep-disordered breathing, particularly those without significant apneas or if events occur primarily in REM sleep or specific positions not well captured at home. Home tests also typically have limited channels compared to a full in-lab polysomnography (PSG), which can provide more comprehensive data.
4. Respiratory Effort-Related Arousals (RERAs): Consider whether the term RDI (Respiratory Disturbance Index), which includes RERAs, was evaluated. If there were RERAs present, they might explain the discrepancy between your symptoms and a normal AHI.
5. Clinical Correlation: It’s important to correlate these findings with your clinical symptoms and history. Persistent symptoms, such as the choking sensation your wife observed and any associated daytime sleepiness or fatigue, should be evaluated further.
Recommendations:
– Follow-Up with a Sleep Specialist: Discuss these findings with a sleep specialist. They might recommend an in-lab polysomnography for a more thorough evaluation, which could include measuring additional parameters like sleep stages and more nuanced respiratory effort assessment.
– Lifestyle and Environmental Modifications: Until further evaluation, consider lifestyle modifications such as weight management, positional therapy (avoiding supine sleep which can exacerbate obstructive events), and avoiding alcohol or sedatives before bed, as these can worsen sleep-disordered breathing.
– Additional Monitoring: In some cases, repeated or more detailed monitoring might be suggested, especially if initial investigations do not clearly explain your symptoms.
Given the complexity and the potential for significant health implications, a detailed clinical assessment is critical to effectively interpret your sleep study results and guide appropriate treatment.
Remember, individualized evaluation and management based on a comprehensive review of both clinical data and personal symptoms are key in sleep medicine.
See less